Laser cutting is based on the high-energy characteristics of laser to realize the cutting operation of materials.
It is a processing technology that cuts materials by irradiating the surface of the material with a laser beam of high energy density, which instantly melts or vaporizes the material.
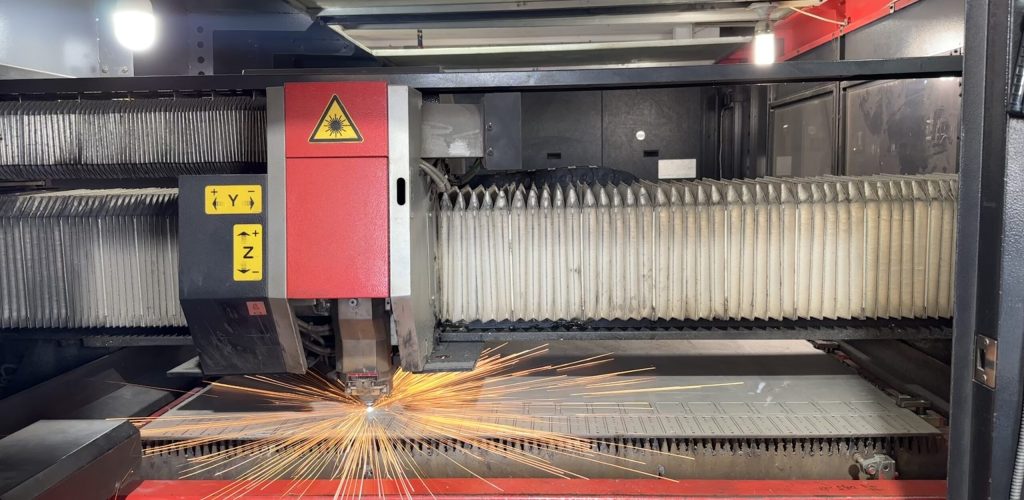

Table of Contents
Features of laser cutting
- High cutting precision
The laser beam can be focused into a very small spot size, usually reaching a tolerance range of millimeters or even smaller. It can precisely cut out complex geometric shapes, thus meeting the extremely high precision requirements for sheet metal processing tasks. - Excellent cutting quality
The precise control of the laser beam energy enables us to make the incision smooth and flat, and we can make its surface roughness reach Ra 1.6 – Ra 3.2μm or even lower.
Meanwhile, we usually keep the heat-affected zone within the range of 0.1 – 0.5mm, which is much smaller than that of traditional cutting methods and this way can preserve the original properties of the materials. - Fast cutting speed
When cutting thin sheet metal materials, the speed of laser cutting can reach several meters per minute or even higher.
Compared with traditional cutting methods, it takes only a fraction of the time to complete the same task, which can significantly shorten the production cycle. - Good applicability
It is applicable to almost all metal materials (such as carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum alloy, copper, etc.), and can also be used for cutting some non-metal materials (such as ceramics, glass, plastic, etc.).
Laser cutting workflow
Preparatory work
Place the materials to be cut on the workbench, and you should adjust the parameters of the laser cutting machine, such as laser power, cutting speed, and focal length, according to the characteristics and requirements of the materials.
Laser generation
The laser generator generates a high energy density laser beam. Common types of lasers include carbon dioxide lasers, fiber lasers, etc.
Laser transmission
The generated laser beam needs to be accurately transmitted to the cutting area. This process is accomplished through the laser transmission system, and there are mainly two common transmission methods:
·fiber-optic transmission
·mirror transmission.
Laser beam focusing
When the cutting head transmits the laser beam, the focusing lens in it will perform the focusing operation on the laser beam. The purpose of focusing is to make the laser beam concentrate its energy onto a tiny area, thus forming a high energy density light spot.
Material melt and vaporize
The focused high-energy-density laser beam irradiates the surface of the material to be cut. The material will quickly absorb the energy of the laser, causing the local part of the material to heat up instantaneously and melt or vaporize.
Silt formation
As the laser beam continuously moves along the preset cutting path, it constantly forms holes on the material surface and connects them one by one, thus forming a continuous and narrow cutting seam.
Auxiliary gas actionser generation
In the laser cutting process, the auxiliary gas plays a very important role. The auxiliary gas system will spray the appropriate auxiliary gas to the cutting area, the common auxiliary gas is oxygen, nitrogen, argon and so on. Different auxiliary gases have different roles in the cutting process:
·Oxygen: When cutting some metal materials (such as carbon steel), oxygen can be used as an auxiliary gas.
·Nitrogen and Argon: When cutting oxidation-prone materials such as stainless steel and aluminum alloy, nitrogen or argon is usually selected as the auxiliary gas.
Cut complete
When the laser beam completely traverses the material to be cut along the predetermined cutting path and forms a complete cutting seam, it successfully cuts the material into the required shape and size. At this point, the laser cutting completes the entire working process.
Clean and maintenance
Regularly clean and maintain the laser cutting machine to ensure its normal operation and extend its service life.
Materials That Laser Can Cut
Metallic material
Non-metallic material
- Ceramic
- Glass
- Plastic
- Wood
- Composite Materials
Laser cutting tolerance
- For thin metal sheet materials (with a thickness less than 3mm):
laser cutting usually manages to control the tolerance within ±0.1mm. - For medium-thickness metal sheet materials (with a thickness ranging from 3mm to 10mm):
laser cutting generally results in a tolerance between ±0.2mm and ±0.3mm. - For thick metal sheet materials (with a thickness greater than 10mm):
laser cutting usually brings about a tolerance between ±0.3mm and ±0.5mm.
Conclusion
Laser cutting, as an advanced and highly efficient processing technology, holds an extremely crucial position in the sheet metal processing industry.
YINLU, being an experienced sheet metal processing manufacturer, is well aware of the significance of laser cutting technology for the enterprise’s production and operation.
Read more about our laser cutting services and request for a quote today.